Ubiquitin-mediated proteolytic
pathway
Most
of the proteins that are degraded in the cytosol are delivered to large protein
complexes called proteasomes, which are present in many copies and are
dispersed throughout the cell.
Each
26S proteasome consists of a central cylinder formed from multiple distinct
proteases, whose active sites are thought to face an inner chamber.
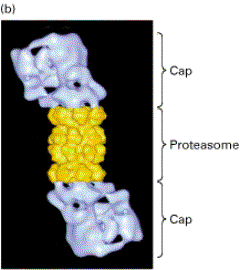
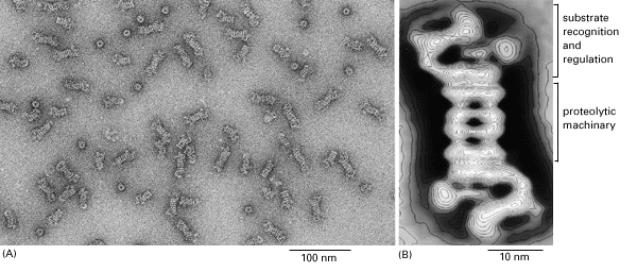
Each
end of the cylinder is "stoppered" by a large protein complex formed
from at least 10 types of polypeptides, some of which hydrolyze ATP.
These protein stoppers are thought to select the proteins for destruction by binding to them and feeding them into the inner chamber of the cylinder, where multiple proteases degrade the proteins to short peptides that are then released.
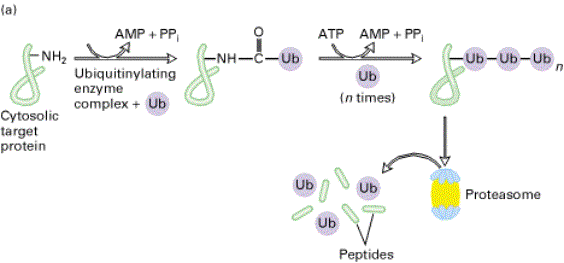
A
conjugating enzyme catalyzes formation of a peptide bond between ubiquitin (Ub)
and the side-chain –NH2 of a lysine residue in a target protein.
Additional Ub molecules are added, forming a multi-ubiquitin chain.