GENE-FOR-GENE INTERACTIONS
For
Necrotrophs: Pathogen
virulence is dominant because of the need to produce a functional
toxin and/or enzyme, whereas avirulence, the inability to cause
disease, is inherited as a recessive trait.
R gene – “anti-dote”
![]()
Disease
![]()
![]()
The
first R gene to be isolated was Hm1 from maize, which
confers resistance to the leaf spot fungus Cochliobolus carbonum.
Hm1 codes for a reductase enzyme that
detoxifies the C. carbonum HC-toxin. This toxin inhibits
histone deacetylase activity and
the Hm1 gene product is thought to inactivate the toxin.

Resistance
to Biotrophs – avirulence and resistance are usually genetically dominant
traits.
More
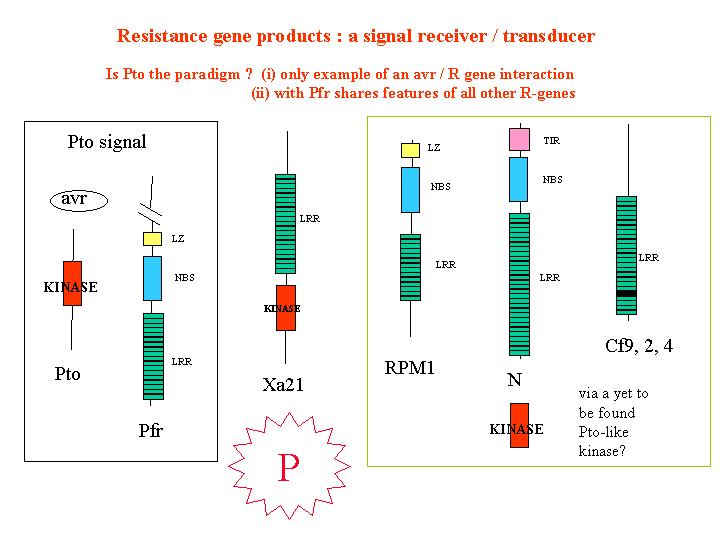
than 20 resistance genes have been cloned which fall into five main classes.
(i)
Detoxifying
enzymes – e.g. Hm1.
(ii)
Intracellular
protein kinases (Pto)- serine/threonine protein kinases
(iii)
Intracellular
Leucine Rich repeats.
LxxLxxLxxLxLxx(N/C/T)c)x)
Lxx/Pxx
Implicated
in protein/protein interactions.
Cf-9
– 23 repeats
Cf-4
– 21 repeats
Cf-2
– 37 repeats
Mutated
RPP5 LRR – abolished Multiple R-gene functions –
Avr
–interacting region? But where is the specificity?
(iiia) With Nucleotide binding site (NBS) and with
Leucine Zipper
NBS – founding in numerous ATP/GTP binding proteins.
Consists of
-
GPGGVGKT-
(P-loop)
-
Asparate
necessary to co-oridinate metal io for phosphate transfer.
-
Arginine
to interact with purine base of ATP. BUT no biochemical evidence.
Leucine Zipper – XDLXXX promotes either dimerisation or
specific interaction with other proteins.
(iiib)With Nucleotide binding site (NBS) with
homology to a domain Toll (insect) and IL-1 receptor (human) receptor. – TIR region.
Significance of this is unknown
(iv)
Membrane
–associated / extracellular protein.
(v)
Kinase
with extracellular Leucine-rich repeats.
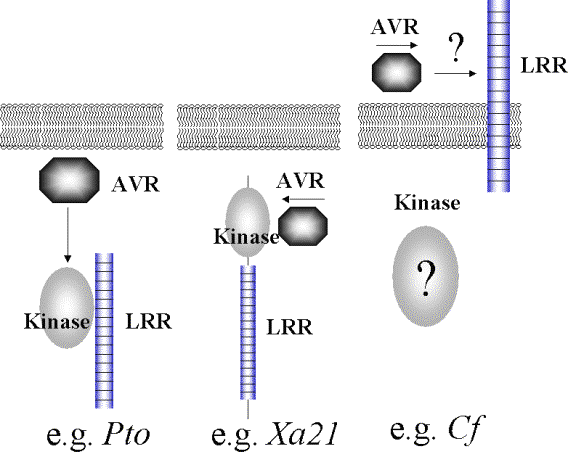
How do R and avr gene
products interact?
Only
with Pto has been shown to directly interact with the avrPto.
BUT
Pto needs to interact with Prf-
a Leucine rich protein to function.
Is
this a model for resistance gene function – The Modular Model?
THIRD HANDOUT: New developments
in our under standing of gene-for-gene interaction.
The “Guard” hypothesis. The RIN4 story
(De
Wit 2002, 416, 810-803)
· RIN4 = RPM1-interacting protein 4
· First identified based on its interaction with avrRpm1-
Isolated
by co-precipitation.
· AvrRpm1 induces the phosphorylation of RIN4.
· RIN4 suppresses defence gene expression
· AvrRpm1 interaction further enhances its suppressive
effects.
· BUT RIN4 is required for RPM1 resistance to bacteria
· and other R genes too!!..avrRpt2 interaction with RPS2.
· Hence, RIN4 is a switch…..and RPM1 “guards” its ability to switch to the
resistant response.
References
de Wit, P. J. (2002). “Plant
biology: on guard.” Nature 416(6883): 801-3.
Mackey et al.,.
(2003). Cell 112(3): 379-89.
Mackey et al.,.
(2002). Cell 108(6): 743-54.