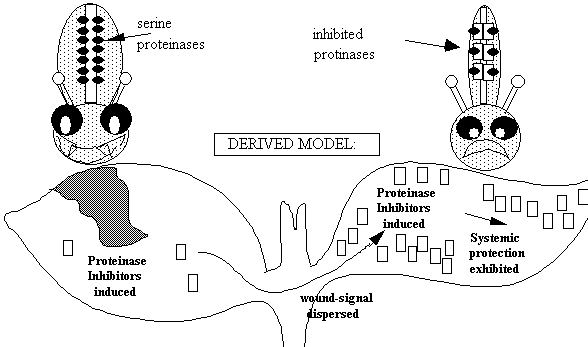
Plant Resistance to Insect Grazing : Proteinase Inhibitors (PI)
Most
effective against proteinases which digest at serine a.a (trypsin).
Rapidly
induced by wounding: mechanical / grazing/ nematode infection of roots…….
...and
subsequently systemically expressed.
Effective
against INSECT LARVAE / NEMATODES where serine proteinase's which are abundant in their digestive
tracts.
Thus,
previous wounding confers protection against further grazing
Proof: Trangenic tobacco plant leaves
constitutively expressing PI's retarded larval development
Has
an obvious biotechnological potential:
PI
are induced during HR but are NOT SA
inducible
-so
are activated by a wound-specific systemic signal.
Systemic signaling
following wounding.
The
“successful” candidate will meet the following criteria.
(1)
Exogenous treatment confer protection and
induce proteinase inhibitors
(2) levels
rise around lesion
(3) systemic
dispersal
(4)
Correlation of signal appearance with protection.
THE
CANDIDATES:
(A) Polygalacturoic acids
(PGAs): .......1,2,3 not 4,5
Radiolabelled
PGA's did not move throughout the plant
...........
therefore a purely local role.
(B) Abscisic Acid :
ABA.......1,2,3
not 4,5
Role
in the control of water relations:
e.g.
ABA level rise during drought conditions.- > ABA closes stomata
In
wound-responses:
(1)
exogenous application of ABA can induce PI
(2)
There is a six-fold rise in ABA concentration upon
wounding in tomato and potato leaves.
(3)
In droopy tomato mutants, deficient
in ABA
synthesis, PI genes are not induced.
No evidence for a role in
systemic movement and other evidence suggests that the role of JA is purely
local.
(C) Systemin: 1,2,3,4 and 5
·
-18aa peptide isolated from
wounded tomato leaves
a potent PI inducer.
·
Only
peptide shown to possess a hormone-like regulatory
function in plants.
·
highly
mobile : 14C-systemin applied to the wound-site was systemically mobilised via the
phloem.
Systemin
is derived from a larger molecule PROSYSTEMIN- 200aa.
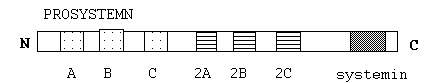
Three
other protein sequences are duplicated.
In
animals: peptide hormones are derived from such a large precursor then
processed to yield more than one biologically active peptide.
Transgenic evidence for
systemin.
- antisense prosystemin gene fused to CaMV 35S
promoter, exhibited reduced (10-20%)
systemic PI
induction.

-
sense transgenes continuously synthesise PI proteins.
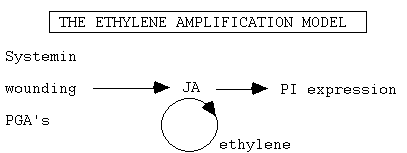
(D) Jasmonic acid.
Membrane derived signals in
wounding
Membrane
damage releases phospholipids mainly
LINOLENIC ACID
Octadecanoid pathway as LA
is an C18:3 lipid
All
downstream enzymes are constitutive : pathways are regulated at the levels of
supply of phospholipids.
Converted
to 13-hydroperoxylinolenic acid, by LIPOXYGENASE (LOX) – an enzyme which introduces a oxygen atom.
LOX
activity increases following infection / wounding/ insect damage.
13-hydroperoxylinolenic
acid serves as a branch point for
the generation of at least three-signal molecules, via further oxidation
1)
Traumatic acid -
First
isolated directly from wounded leaves and shown to enhance cell-proliferation
at the wound-site.
2)
Hexanal and hexanols – also known as “green leaf
volatiles”
Saturated
and unsaturated six carbon alcohols, aldehydes and esters.
Constitutively
produced – may be stored in specialized glands or in trichomes.
Toxic
products of fatty acid oxidation. produced in large quantities.
Active
against fungi, bacteria, insects and possibly the host itself. May represent
part of a cell-death mechanism
3)
Jasmonic acid
Emerging
as the major intracellular wounding signal.
Exogenous
application of JA induces,
(1)
proteinase inhibitors
(2)
Phenylpropanoid enzyme genes
(3)
extensins, glycine-rich proteins
JA
has been recently reported as accumulating during HR.
In Nicotinia attenuta – JA increases the
abundance of nicotine. This is
naturally synthesized in the roots and mobilized systemically but is also
synthesized in leaves following wounding.
This results in a 90% reduction in leaf loss with
MeJA treatment to grasshopper (Trimerotrophs pallidipenni)
but
at what cost?
·
6%
of all nitrogen end—up in nicotine.
·
nicotine
is also effective against insect carnivores
and parasitic wasps – so lose an trophic level in defence.
·
Seed
product was reduced by 26%
However,
when considering the loss resulting from insect damage their was a net overall
increase in plants able to produce viable seed.
-
so
JA defences are costly but worth it!
The role of Ethylene
:
(1)
developmental - fruit ripening
(2)
In defence. Application of ethylene induces
- PR
protein genes.
-
lignification, by activating phenylpropanoid enyzmes and
extensins.
Ethylene produced quickly after infection
or wounding.
Proteinase Inhibitors and ethylene
Gassing
with ethylene had no effect on PI induction.
BUT
applying systemin and JA to suspension cultures cells induced both ethylene and
proteinase inhibitors. ----????
Also
: PI induction was blocked with inhibitors of ethylene synthesis AND reduced JA synthesis
how can you
explain this?
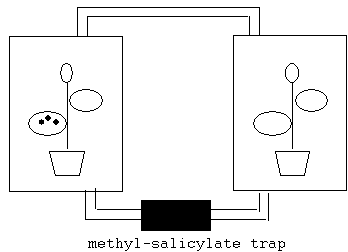
Interplant acquired resistance
Signaling
via gaseous signals
(A) Ethylene : exists exclusively as a gas...
(B) Methyl-jasmonate : volatile
Able to induce systemic PI expression.
Sagebrush
produces copious amounts of jasmonic acid...and can induce PI genes in adjacent
plants.
(C) Methyl-salicylate : volatile
detected during SAR
induces PR gene expression
Can
induce SAR.
BUT An ironic situation –
It
may be that you cannot have systemic resistance to pathogens cannot co-exist
with systemic expression of PI.