The Biotrophic form of Pathogenesis
LIFE CYCLE
Virulence determinants are different in biotrophic
forms of
pathogenesis
Toxins
1.
Mostly
small peptides
2.
Unlike
fungal toxins, these do not exhibit host-specificity
3.
Also
unlike fungal toxins, virulence, not pathogenicity functions.
·
A
toxins are produced by non-pathogenic strains of P.syringae
·
Some
biosynthetic genes may be mutated without loss of
pathogenicity.
4.
Syringomycin
/ coronatine are part synthesised by non-
ribosomal
means.
Toxins Produced
by Pseudomonas syringae pathovars
Toxin |
Pathovar |
Function or Target |
Symptoms |
Syringomycin
|
syringae |
Forms pores in
plasma membrane
|
Necrosis
|
Syringopeptin
|
syringae |
||
Coronatine
|
e.g. tomato, |
Molecular
mimic of the plant signal, jasmonic acid. |
Chlorosis
|
Tagetitoxin
|
tagetis |
Inhibitor
of chloroplast RNA polymerase |
Chlorosis
|
Phaseolotoxin
|
phaseolicola |
Inhibitor
of ornthine carbamoyltransferase |
Chlorosis |
Tabtoxin
|
tabaci |
Inhibitor of glutamine
synthase
|
Chlorosis
|
Phaseolotoxin – causes halo’s in French bean blight
-
a tripeptide – ornithine-
alanine – arginine (with a
phosphosulphinyl group).
-
ornthine
carbamoyltransferase – normally converts
ornithine to citrulline – an
arginine precursor.
-
Inhibiton
by Phaseolotoxin depletes citrulline-
arginine – Elevates ornithine.
-
Changes the permeability of
membranes
Tabtoxin
Tabtoxin minus mutants show reduced virulence – causing
necrotic spots without chlorosis.
A dipeptide composed of
threonine and the unique amino acid – tabtoxinine.
Hydrolysed in plant cell and tab-toxinine inhibits glutamine
synthase.
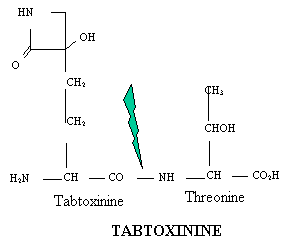
Reduces glutamine levels and increased the
concentration
of ammonia.
Ammonia inhibits photosythesis and destroys the
thylakoid
membrane of the chloroplast. This lead to chlorosis and eventually
necrosis.
Also suppresses plant defences.
· Extracellular polysaccharide (EPS).
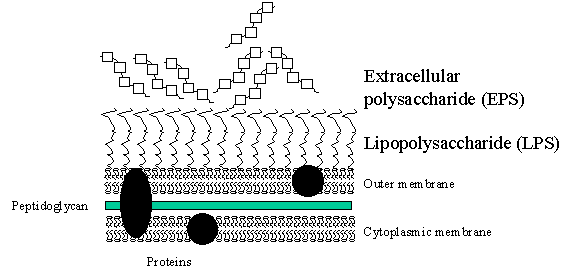
In Pseudomonas (Ralstonia) solanacearum
1
Extracellular
polysaccharide occurring as a capsular material surrounding the bacterial cell
or may be spread as a fluvial slime,
2
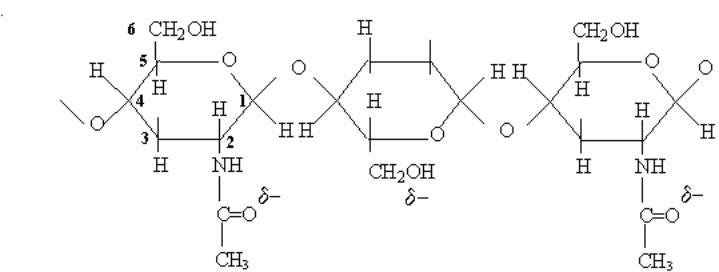
Linear polymer of
three types of sugars e.g.
N-aceylgalactosamine .
d-
3
Therefore
a highly charged polymer…viscous.
4
Produced
to high levels in planta.
5
Functions
·
Protects
bacteria from desiccation
·
Concentrates
minerals and nutrients
·
Enhances
attachment to surfaces
·
Acts
a virulence determinant, sustaining water-soaking
and blocks
xylem resulting in wilt