The application of Science?
Case Number 1. Mimics of
systemic acquired resistance.
A
new form of agro-chemical: Elicitors of SAR in the field.
SA
is rapidly broken down and is too toxic.
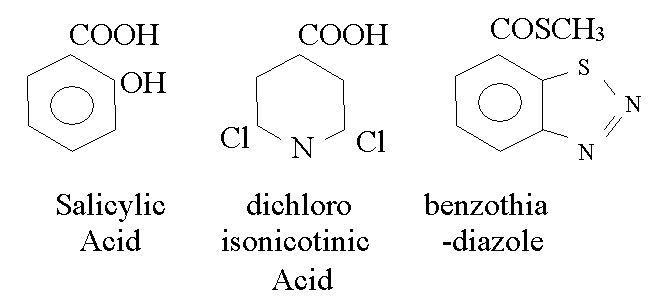
In
the field the promise of BTH has not been fulfilled for cereal crops.
Now
targeted use – Mango, Banana, tomato and tobacco.
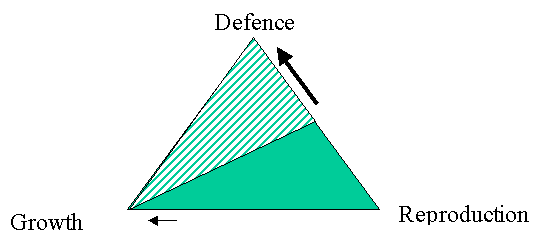
BUT
what is the cost –
Also
BTH treatment suppresses plant anti-insect measures.
Case 2: Protection against insects: BT toxin
The
Problem:
Crop
Loss through insect grazing ($ Million)
(% of total crop where
known)
![]()
Cotton 1870
Fruit
and Vegetables 2465 (6%)
Rice 1190
(27%)
Maize 620
(12%)
Other 1965
Insecticide
Expenditure ($ Million)
![]()
Rice 45000
Vegetables 25000
Fruit 20000
Maize 8000
•Bacillus
thuringensis forms toxin crystals (Cry) during sporulation
